Tecno-Plast Srl acquired the Industry 4.0 Certificate ![]()
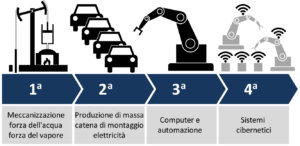
Industry 4.0 is the tendency of industrial automation to introduce new production technologies in order to improve working conditions, to create new business models and to improve production and system quality. Researchers do not agree about working conditions. Some believe that an improvement in working conditions would be just a promise, which can be found in every technical transformation.
The smart factor.
Industry 4.0 follows the smart factor concept which is composed of 3 parts:
- Smart production: new technologies which assemble all production elements (operator, machines and instruments).
- Smart service: not only IT and technical facilities which integrate systems but also all the facilities which combine companies (supplier – customer) and to other facilities (streets, hubs, recycling etc..).
- Smart energy: we pay attention to energy consumption, creating more performing systems and reducing energy waste according to sustainable energy rules.
An Industry 4.0 key point is the cyber-physical system (CPS). CPS is the physical system which is strictly connected to an IT system and which can interact and collaborate with other CPS systems. This is fundamental for devolution and the system interaction and this is strictly connected with an Industry 4.0 concept.
Key Enabling Technologies
From research by Boston Consulting it emerged that some 4th industrial revolution is based on so called “enabling technologies”. Some of these are already known but they have never overcome division between applied research and real production. Today, thanks to the systems interaction, the global market is changing by mass customization and it appeals to the manufacturing industry.
The 9 key enabling technologies named by Boston Consulting are:
- Advanced manufacturing solution: advanced production systems, aka modular interconnected systems which guarantee flexibility and performance. Examples of these technologies are automated material handling systems and advanced robotics, which can be found on the market nowadays as collaborative robot or cobot.
- Additive manufacturing: additive production systems which increase material use efficiency.
- Augmented reality: augmented vision to better guide operators in their daily activities.
- Simulations: simulation between interconnected machines to optimize processes.
- Vertical and horizontal integration: horizontal and vertical integration and exchange of information among production process components.
- Industrial internet: communication amongst production elements, not only inside the company, but also externally thanks to the internet.
- Cloud: development of cloud technologies facilitating online information archiving, the use of cloud computing and data analysis services etc.. Parts of the cloud are also management techniques of huge data quantity through open systems.
- IT Security: increase of internal and external connections requires information and systems security, which must not be altered by external parties.
- Big Data Analytics: management of huge data through open systems which allow predictions and expectations.
Industry 4.0 Observatory of Politecnico di Milano gives another classification of 6 key enabling technologies, called “smart technologies” and it divides them into 2 main groups of innovative digital technologies: information technologies (IT) and operational technologies (OT).
The information technologies (IT) group is comprised of:
- Industrial Internet of Things: smart objects and smart net technologies.
- Industrial Analytics: technologies which use large data with hidden information.
- Cloud Manufacturing: cloud computing usage for manufacturing.
The operational technologies (OT) group is comprised of:
- Advanced Automation: robotic-like technologies using the latest-automated production systems.
- Advanced Human Machine Interface (HMI): wearable devices and the latest human-machine interfaces.
- Additive Manufacturing: technologies similar to types found by Boston Consulting.
According to research by Federmeccanica published in 2016, the use of key enabling technologies should reduce time to market and customised offer costs, with more benefits in terms of productivity and available information about production processes.